Publications
A collection of my research work.
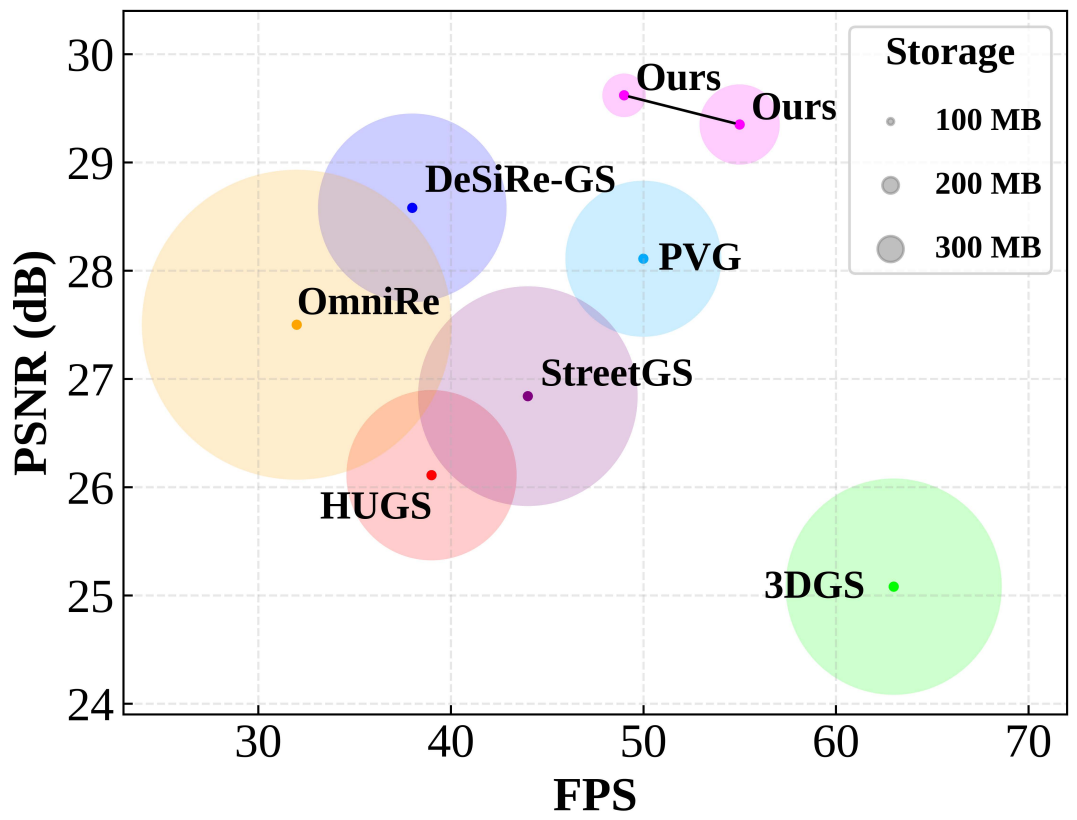
HDGS: Hierarchical Dynamic Gaussian Splatting for Urban Driving Scenes
Fudong Ge, Jin Gao, Hanshi Wang, Yiwei Zhang, Ke Wang, Weiming Hu, Zhipeng Zhang
AAAI 2026Oral
Dynamic-scene 3D Gaussian Splatting faces a fidelity--storage trade-off in urban driving. We propose Hierarchical Dynamic Gaussian Splatting (HDGS) with multi-layer anchors to model moving objects while enforcing global--local and depth-consistency constraints, enabling efficient high-fidelity compression.
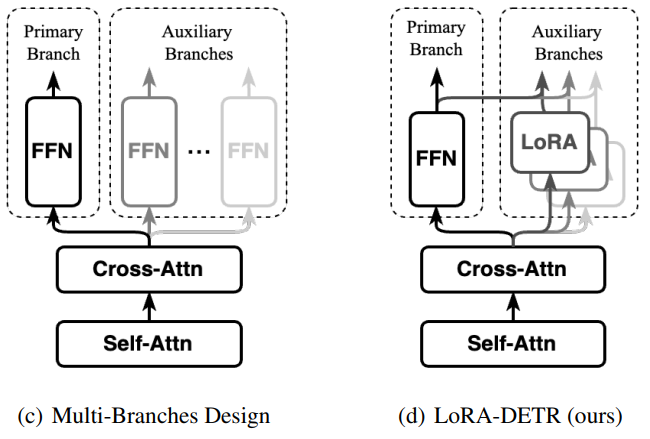
Integrating Diverse Assignment Strategies into DETRs
Yiwei Zhang, Jin Gao, Hanshi Wang, Fudong Ge, Guan Luo, Weiming Hu, Zhipeng Zhang
AAAI 2026
One-to-one matching in DETR leads to slow convergence and sensitivity to assignment choices. We introduce LoRA-DETR with stage-wise assignment via LoRA; each stage adopts a different complementary strategy and supervises later stages to stabilize training and enrich features, improving accuracy across datasets.
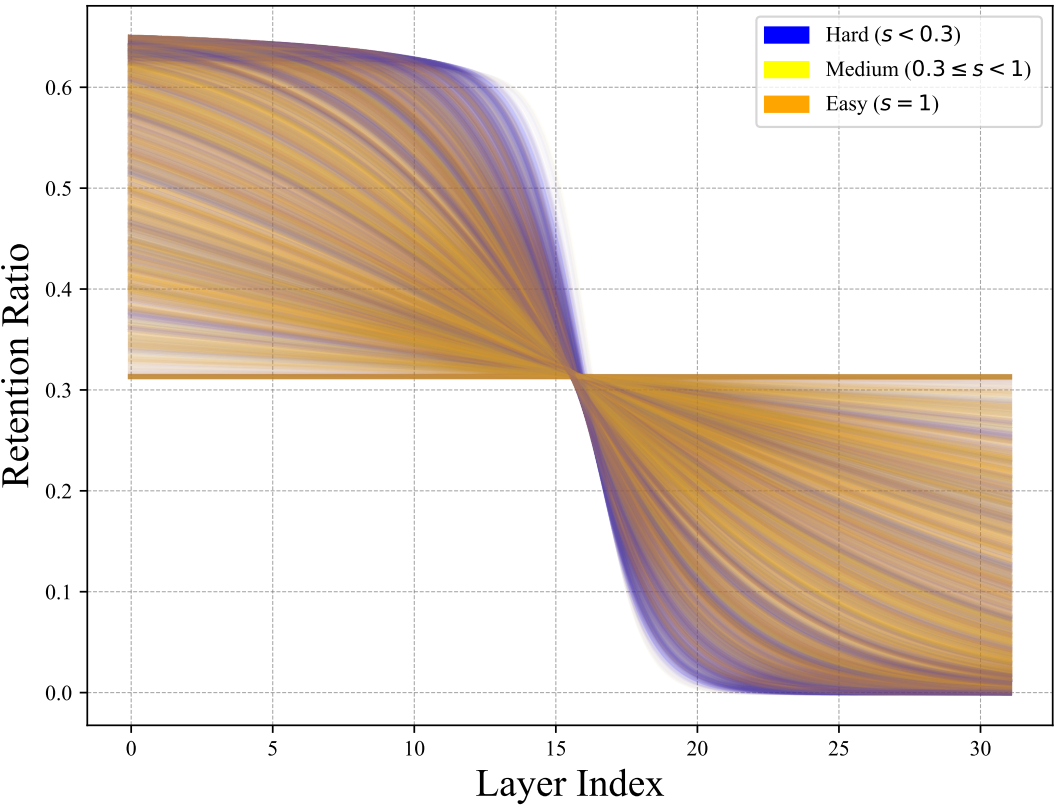
AutoPrune: Each Complexity Deserves a Pruning Policy
Hanshi Wang, Yuhao Xu, Zekun Xu, Jin Gao, Yufan Liu, Weiming Hu, Ke Wang, Zhipeng Zhang
NeurIPS 2025
Motivation: VLMs for vision-language and end-to-end driving suffer from long visual sequences that raise memory and latency, while training-free pruning often uses fixed schedules without global compute control, which limits reasoning-heavy tasks. Method: AutoPrune estimates mutual information between early visual and textual tokens and maps it to a budget-constrained logistic retention curve, yielding per-sample and per-task token keep ratios across layers under any target token/FLOPs budget. Results: On LLaVA 1.5 7B and other VLM/VLA models, AutoPrune removes up to 89% visual tokens and cuts FLOPs by 76.8% while retaining 96.7% average accuracy, surpassing PDrop by 9.1% with consistent gains on VLM benchmarks and autonomous driving.
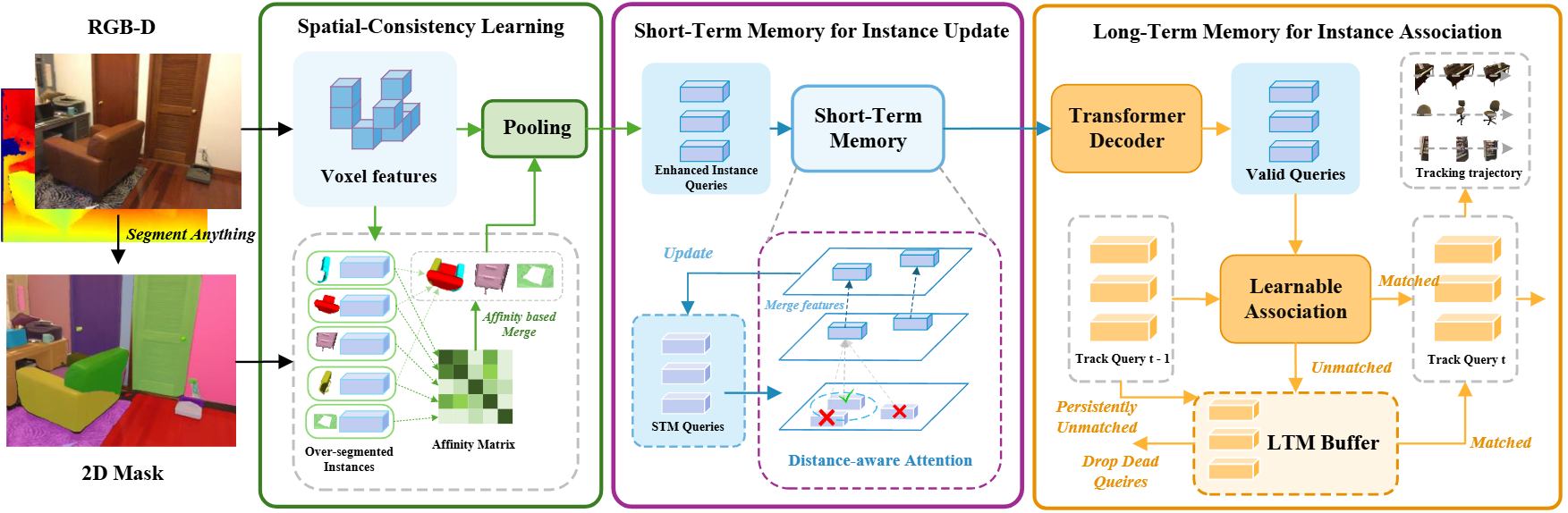
Online Segment Any 3D Thing as Instance Tracking
Hanshi Wang, Zijian Cai, Jin Gao, Yiwei Zhang, Weiming Hu, Ke Wang, Zhipeng Zhang
NeurIPS 2025
Motivation: Online 3D instance segmentation with VFMs often yields fragmented masks, over-segmentation, and identity drift due to missing temporal modeling. Method: Recast as tracking with three modules—LTM (bounded track bank with confidence-gated Hungarian assignment), STM (distance-aware cross-frame attention for short-term context), and SCL (merge high-affinity fragments with joint 2D/3D reasoning and one-to-many supervision). Results: On ScanNet200, improves ESAM by 2.8 AP with real-time throughput and consistent gains on ScanNet, SceneNN, and 3RScan.
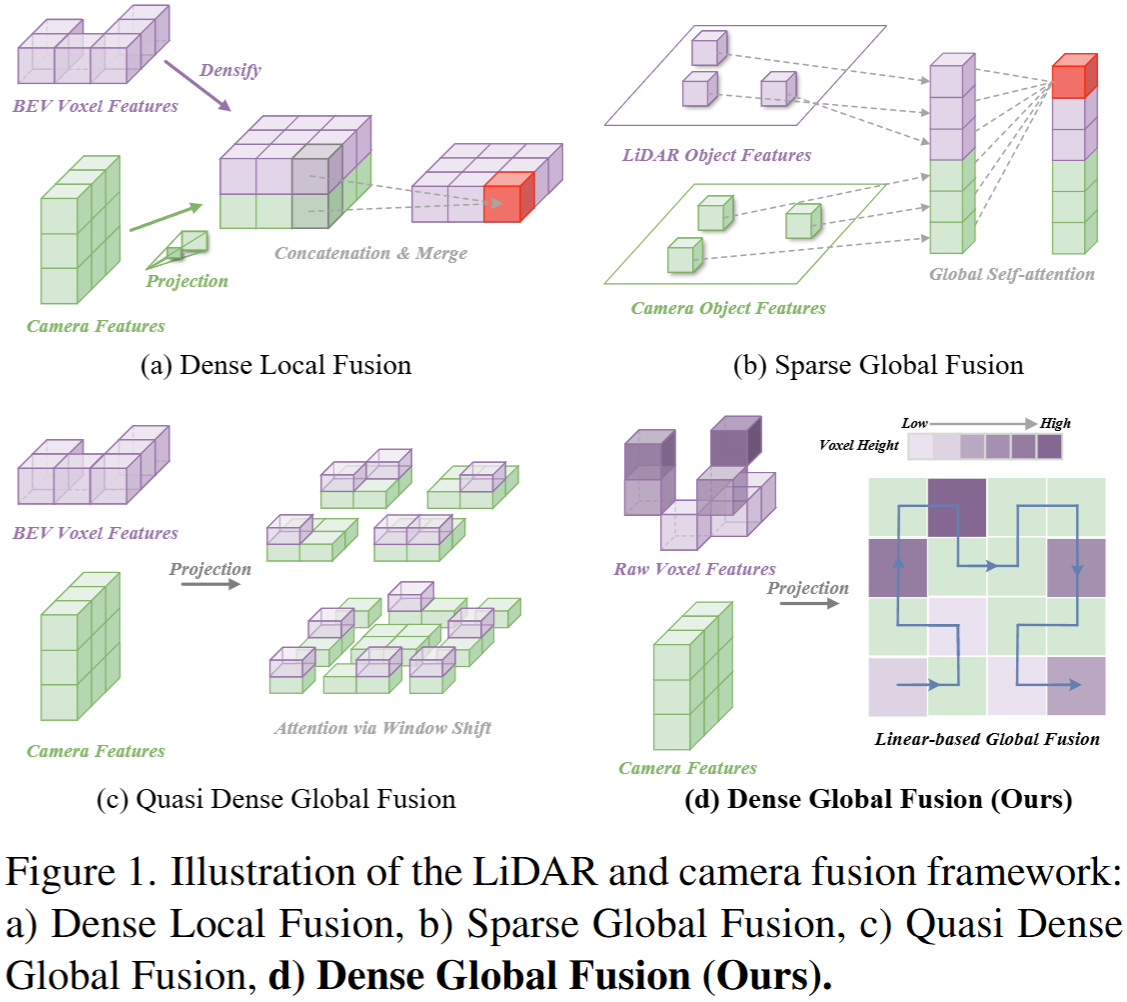
Height-Fidelity Dense Global Fusion for Multi-modal 3D Object Detection
Hanshi Wang, Jin Gao, Weiming Hu, Zhipeng Zhang
ICCV 2025Highlight
Motivation: In camera+LiDAR multi-modal 3D detection, existing methods struggle to jointly achieve efficiency, long-range modeling, and full-scene retention. Method: A set-based fusion using linear attention (Mamba) with Height-Fidelity LiDAR encoding and a Hybrid Mamba Block to align modalities, preserve height cues, and learn local/global context. Results: On nuScenes val, achieves 75.0 NDS, surpassing SOTA with faster inference; ICCV 2025 Highlight.
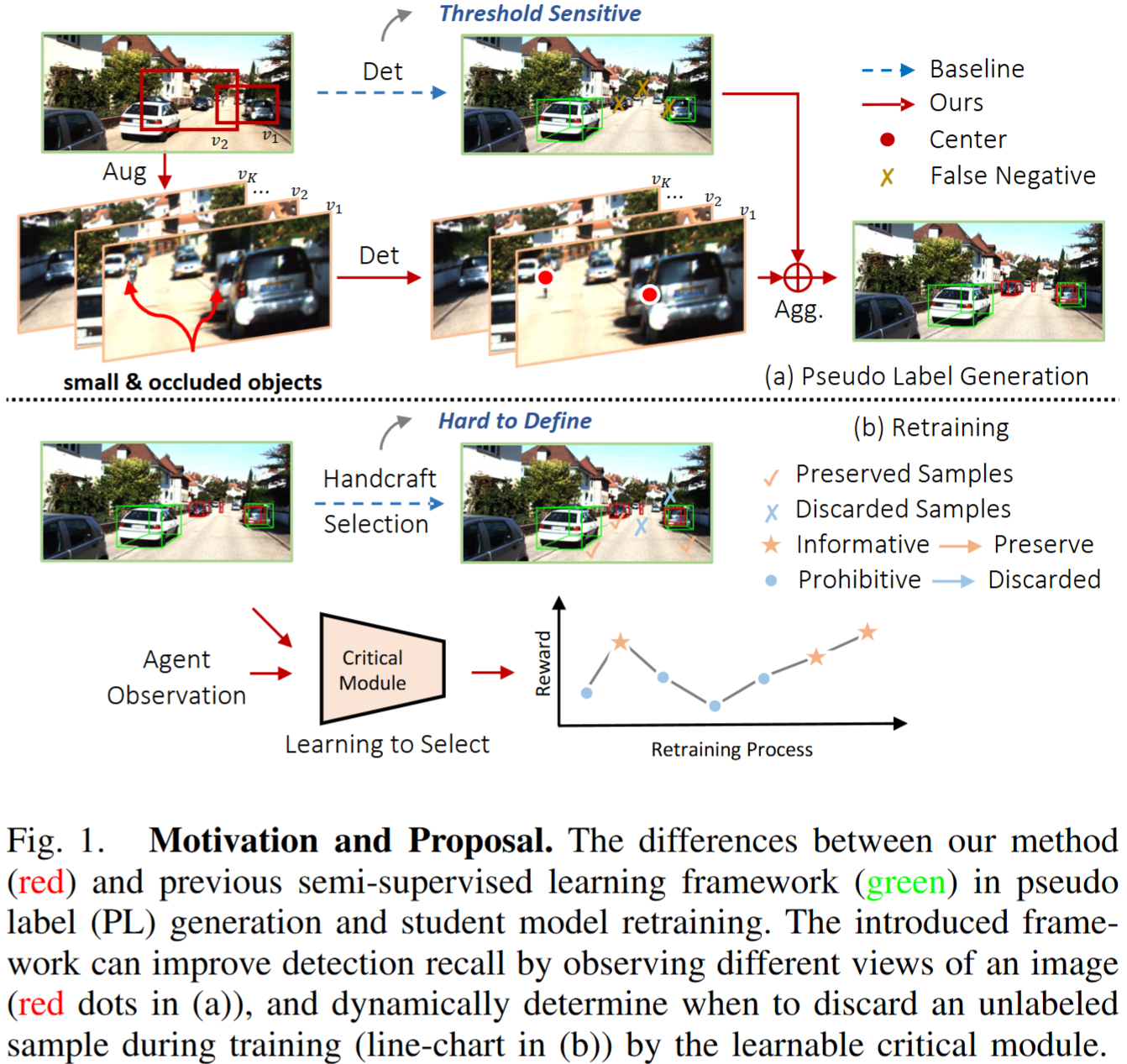
The Devil is in the Quality: Exploring Informative Samples for Semi-Supervised Monocular 3D Object Detection
Zhipeng Zhang†, Zhenyu Li†, Hanshi Wang†, Yuan He, Ke Wang, Heng Fan
ICRA 2025
Motivation: Semi-supervised monocular 3D detection suffers from noisy pseudo-labels and low learning efficiency. Method: Augment-Criticize strategy learns transformations and aggregates predictions to mine reliable pseudo-labels; Critical Retraining Strategy dynamically evaluates pseudo-label contributions to suppress noise. Results: Applied to MonoDLE and MonoFlex, yields significant gains, showing effectiveness and generality.
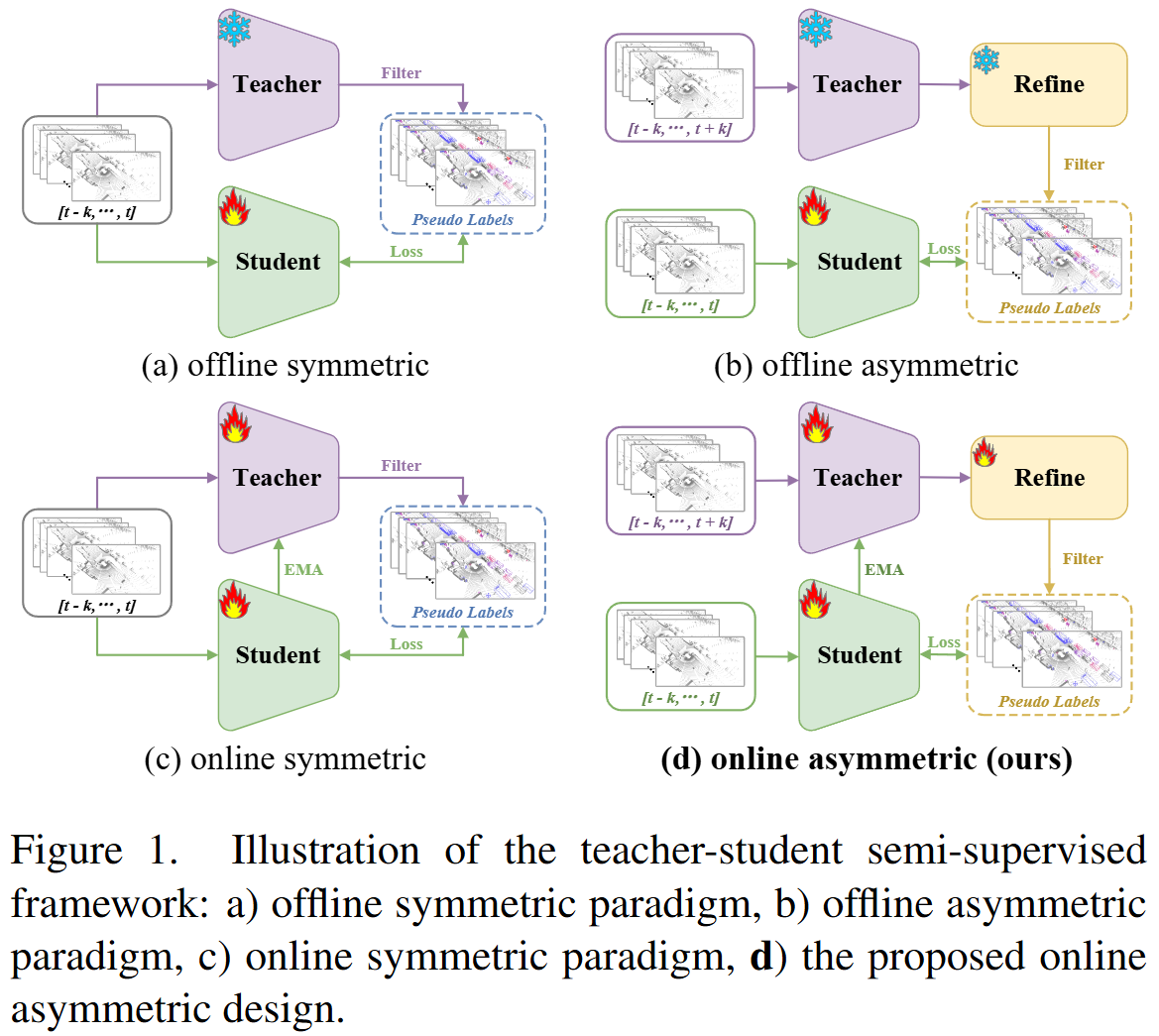
A-Teacher: Asymmetric Network for 3D Semi-Supervised Object Detection
Hanshi Wang, Zhipeng Zhang, Jin Gao, Weiming Hu
CVPR 2024
Motivation: Teacher/student architectural and input-format symmetry weakens distillation and under-utilizes temporal cues. Method: First online asymmetric semi-supervised 3D detection framework with attention-based refinement, leveraging past/future cues in a divide-and-conquer strategy to correct poor detections, misses, and false positives. Results: On Waymo, boosts mAP (L1) by 4.7 over prior SOTA with fewer training resources.